Dr Newaj and Dr Eve
Rosacea is a chronic relapsing skin disorder characterized by facial flushing, persistent redness of the face, small arteries becoming visible on the face, and acne-like lesions affecting the central face. It can also affect the nose and the eyes.
This disease starts in ones twenties and progresses with time. It affects all races, though it is more visible in white skin. An interesting fact of this condition is that the nose can increase in size, but patients usually do not notice this.
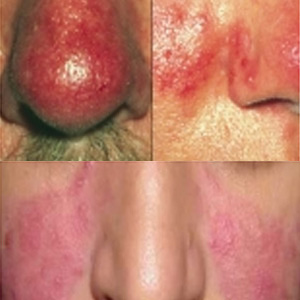
Rosacea is quite commonly encountered in a dermatology practice. Basically, the arteries supplying the face become hyperactive and increase the blood flow to the affected areas. This results in an increase in nutrients and growth factors, which stimulates the sebaceous glands to enlarge. There is growth of many small capillaries on the face and eyes. The main presentation is that of small arteries on the face or a persistent blush.
The National Rosacea Society has described a classification system based on 4 main subtypes:
- The erythematotelangiectatic type is characterised by frequent blush and the appearance of small capillaries on the face.
- The papulopustular type looks very similar to Acne and can only be differentiated by a dermatologist.
- As for the phymatous type, the nose becomes red, rough and increases in size( more common in males).
The eyes are affected in about 25% of cases, whereby the person feels a constant irritation of the eyes. They also get injected and red.
- The granulomatous variant looks like severe acne and can cause permanent skin damage. This disease can contribute to lower self-esteem and have significant psychosocial implications, e.g. stress at work and social isolation. This can have a significant impact on quality of life.
Once established, the disease tends to progress and cause permanent damage to the cheeks, nose and eyes. Therefore early diagnosis and treatment is very important.
What are the trigger factors?
Anything that can cause vasodilatation (widening) of the arteries of the face, should be avoided. Too much hot coffee, tea etc., smoking, alcohol and spicy foods have all been implicated. However, the sun can also aggravate the disease; therefore a strong sunscreen is required. In some patients, the disease can be controlled by simple habit modification and lifestyle changes.
However, others need medication and regular dermatology follow-up. Medications include Doxycycline, sulphur creams, metronidazole gel, azelaic acid creams and in severe cases, low doses of oral retinoids. These treatments are lifelong and needs to be modified according to response. In some cases, patients do benefit from laser therapy, however, this also requires repeated treatment.
In brief, Rosacea is a fairly common disease and treatment is available. One needs to understand that it is chronic and can damage the facial skin if left untreated.
Sources:
Dr Rakesh Newaj and Dr Eve: Rosacea series
*The content in this article does not necessarily reflect the views of the sponsor.
This disease starts in ones twenties and progresses with time. It affects all races, though it is more visible in white skin. An interesting fact of this condition is that the nose can increase in size, but patients usually do not notice this.
Rosacea is quite commonly encountered in a dermatology practice. Basically, the arteries supplying the face become hyperactive and increase the blood flow to the affected areas. This results in an increase in nutrients and growth factors, which stimulates the sebaceous glands to enlarge. There is growth of many small capillaries on the face and eyes. The main presentation is that of small arteries on the face or a persistent blush.
The National Rosacea Society has described a classification system based on 4 main subtypes:
- The erythematotelangiectatic type is characterised by frequent blush and the appearance of small capillaries on the face.
- The papulopustular type looks very similar to Acne and can only be differentiated by a dermatologist.
- As for the phymatous type, the nose becomes red, rough and increases in size( more common in males).
The eyes are affected in about 25% of cases, whereby the person feels a constant irritation of the eyes. They also get injected and red.
- The granulomatous variant looks like severe acne and can cause permanent skin damage. This disease can contribute to lower self-esteem and have significant psychosocial implications, e.g. stress at work and social isolation. This can have a significant impact on quality of life.
Once established, the disease tends to progress and cause permanent damage to the cheeks, nose and eyes. Therefore early diagnosis and treatment is very important.
What are the trigger factors?
Anything that can cause vasodilatation (widening) of the arteries of the face, should be avoided. Too much hot coffee, tea etc., smoking, alcohol and spicy foods have all been implicated. However, the sun can also aggravate the disease; therefore a strong sunscreen is required. In some patients, the disease can be controlled by simple habit modification and lifestyle changes.
However, others need medication and regular dermatology follow-up. Medications include Doxycycline, sulphur creams, metronidazole gel, azelaic acid creams and in severe cases, low doses of oral retinoids. These treatments are lifelong and needs to be modified according to response. In some cases, patients do benefit from laser therapy, however, this also requires repeated treatment.
In brief, Rosacea is a fairly common disease and treatment is available. One needs to understand that it is chronic and can damage the facial skin if left untreated.
Sources:
Dr Rakesh Newaj and Dr Eve: Rosacea series
*The content in this article does not necessarily reflect the views of the sponsor.




 Publications
Publications
 Partners
Partners