It has been proven that diabetics have a higher risk of blindness and other eye problems.
However, with the correct care and intervention you can protect your eyes and detect any complications before they affect your vision.
The link between diabetes and the eyes
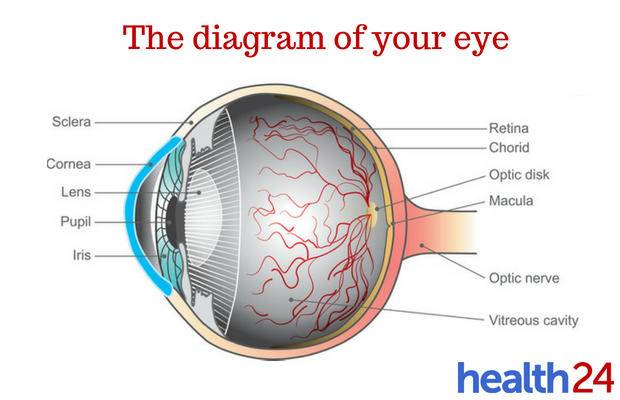
To understand the link between diabetes and eye problems, it’s important to understand how your eye works.
Your eye is protected by a tough outer clear membrane, called the cornea. It protects the eye while letting light pass through.
After light passes through the cornea, it goes through the pupil to a space called the anterior chamber and onward to another lens that enables you to focus on objects. The light then passes through another chamber in the centre of the eye and finally travels to the retina at the back of the eye.
The image is now captured and sent to the brain to be decoded. The macula, an important part of the retina, enables you to see clearly. This part is nourished by the nervous system and tiny blood vessels.
Having chronic high blood sugar levels caused by diabetes can cause damage to the nervous system and tiny blood vessels throughout the body, including those in the eyes. This can lead to several eye complications. The blood vessels can also start leaking fluid, which can cause swelling in the eye.
What are the different eye problems you may encounter?
Diabetic eye disease includes a variety of eye conditions that can occur in people with diabetes and includes the following:
- Diabetic retinopathy: A condition that affects the blood vessels in the retina that line the back of the eye.
- Diabetic macular oedema: Swelling of an area in the retina, called the macula, caused by the build-up of fluid.
- Cataracts: The clouding of the normally transparent crystalline lens in the eye, causing blurry vision.
- Glaucoma: The occurrence of abnormally high pressure in the eye because of too much liquid. This can cause damage to the optic nerve.
According to the journal Eye and Vision, globally diabetic retinopathy is one of the biggest causes of blindness.
Who is at risk for diabetic eye complications?
The Global Diabetes Community says that anyone with diabetes (type 1, 2 or gestational) is at risk for eye complications, and the risk increases the longer you have diabetes.
Any diabetes-related eye complication can lead to partial or complete loss of vision if left untreated.
When should you immediately consult a medical professional?
Most eye complications usually have no symptoms in the beginning, but as they progress, they will start affecting vision. Bleeding from abnormal blood vessels in the retina can cause the appearance of dark spots in your vision (often called “floaters”).
Although these dark spots can disappear on their own, they can also signal the risk of retinal bleeding, which can cause permanent loss of vision.
Other signs and symptoms that should be immediately checked out include:
- Sudden blurry vision – this could be caused by your insulin dosage, which may need to be adjusted
- Sudden sharp pain in your eye, which can signal pressure
- Sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes
- Any flashes of light
- Any nausea, vomiting or headaches accompanying eye complications
What are the treatment options?
There are a couple of options to correct vision loss and retina damage. These include:
- Laser treatment in the case of severe retina damage.
- A surgical procedure called vitrectomy to treat bleeding in the eye, scar tissue around the eye and retinal detachments.
- Injection or oral medication to repair blood vessels and help bring down swelling.
Keep your eyes in tip-top shape
Early detection and treatment can reduce a diabetic’s risk of blindness by 95%. Here are a few things you can do to monitor your eye health:
- Have a comprehensive eye test once a year, or more frequently if you already have eye complications.
- Control your blood sugar and insulin, as this slows the onset of diabetic retinopathy and other eye conditions.
- Include plenty of fruits and vegetables in your diet and include exercise in your daily routine to keep your nervous system healthy.
- Check your cholesterol levels, as too much “bad cholesterol” (LDL) can cause damage to blood vessels.
- Keep your blood pressure under control, as high blood pressure increases your risk for glaucoma.
Image credit: iStock




 Publications
Publications
 Partners
Partners











